Circle Introduces Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol: Becoming the On-Chain Visa, Ending Cross-Chain Bridge Hacks
#528
GM,
First, I want to thank the 30 readers who have already participated in the voting, helping Blocktrend to obtain Gitcoin Grants matching funds. Last weekend, I added two hand-drawn illustrations to "Quadratic Funding: A Tax System Supporting Public Goods Development" to help unfamiliar readers easily understand the operation mechanism of quadratic funding.
Recently, Ethereum's transaction fees have been relatively high, making it unsuitable for small transactions. Gitcoin also urges everyone not to rush to check out and wait to see if the transaction fees will drop before the event ends on May 9th.
High Ethereum transaction fees are no longer news. Ethereum is like downtown Taipei—convenient for living but with high housing prices. Those who cannot afford it will move to surrounding cities and commute. In the digital world, "commuting" relies on cross-chain bridges. However, in recent years, cross-chain bridges have often become targets for hackers, and there are many operational "nuances."
Last week, Circle, the issuer of USDC, launched a brand new cross-chain infrastructure called the "Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol" (CCTP). This not only significantly reduces the financial losses caused by cross-chain bridge hacks but also makes cross-chain applications more intuitive. This article will explain how CCTP works and what benefits it brings to Circle?
Exchanges and Cross-Chain Bridges
The existence of cross-chain bridges indicates that the Web3 infrastructure is not yet mature.
Blocktrend members must have experience with cross-border shopping. The Substack service used by Blocktrend requires payment in US dollars, but for the vast majority of people, there isn't much difference between Blocktrend receiving US dollars or New Taiwan dollars. When swiping the card, Visa automatically converts the New Taiwan dollars to US dollars for the reader. A few days later, I receive US dollars in my US collection account, and your payment account will be charged the equivalent amount in New Taiwan dollars.
Such everyday cross-border and cross-currency transactions are quite complicated in the blockchain world.
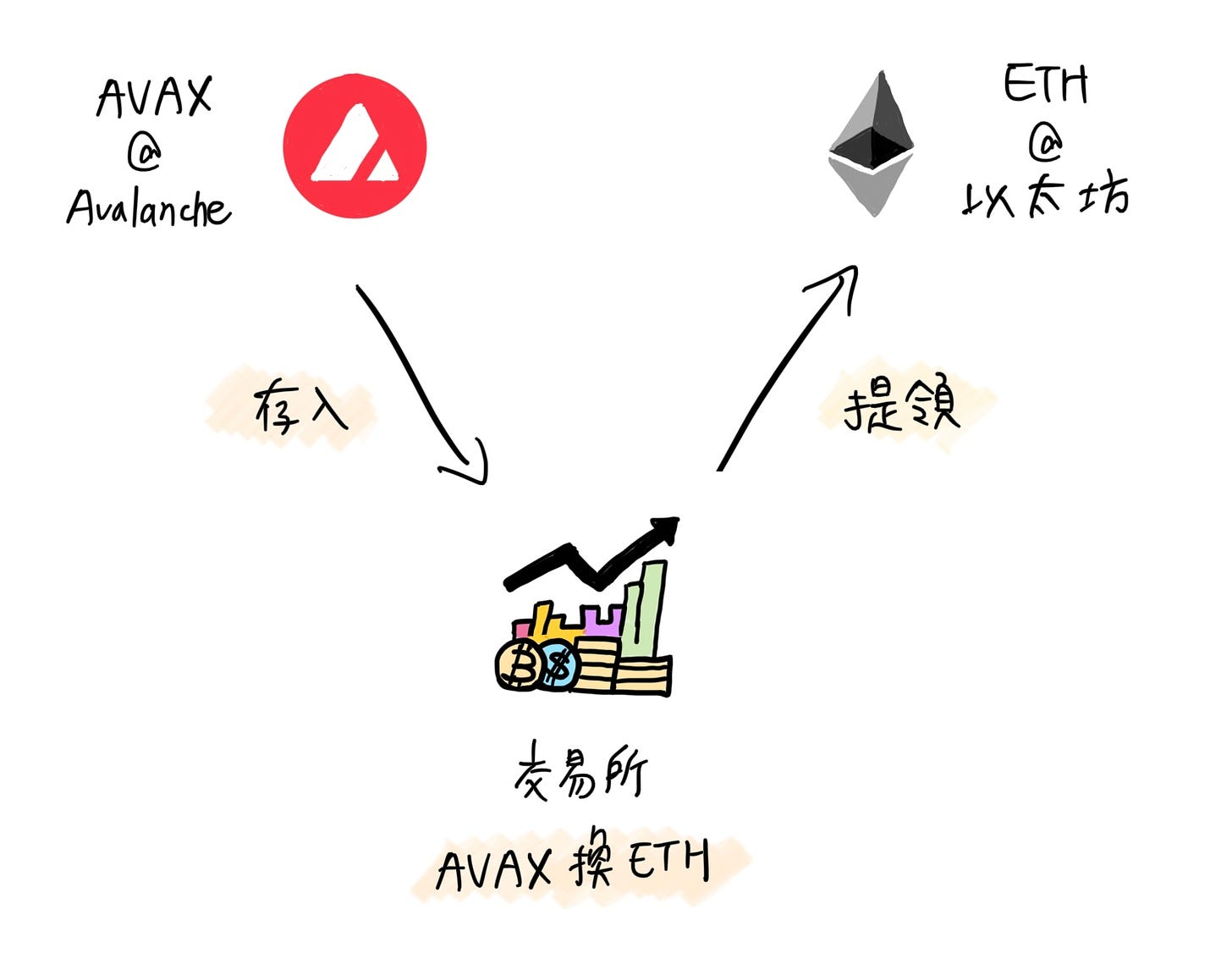
Take this Gitcoin Grants event as an example; it only accepts voting with Ethereum blockchain's ETH and DAI cryptocurrencies. If you only have AVAX on the Avalanche blockchain and want to participate in the voting, the ideal process should be like swiping a card across borders – regardless of the chain or currency, the other party can ultimately receive ETH or DAI. Unfortunately, there is no "Visa" on the chain to handle this, so people have to do it themselves.
Most people choose centralized exchanges, depositing AVAX first, exchanging it for ETH, and then withdrawing it to Ethereum. However, not all exchanges support the Avalanche blockchain for deposits. In addition, the withdrawal time and fees vary for each exchange. Just finding a suitable exchange, from deposit, trading, withdrawal to completing the vote, may take up to an hour.
If operating with a decentralized cross-chain bridge, one has to exchange AVAX for ETH on a decentralized exchange first and then transfer it to Ethereum via the cross-chain bridge. Although the operation process is much simpler, it is not popular because there are too many details to pay attention to.
Cross-chain bridges are like cross-border currency exchange services. Using a US dollar transfer as an analogy, transferring ETH via a cross-chain bridge is like transferring US dollars from the United States to Taiwan. However, what Taiwan actually receives is not US dollars, but an equivalent US dollar certificate issued by E.Sun Bank (for example). Moreover, various banks in Taiwan will issue their own US dollar certificates.
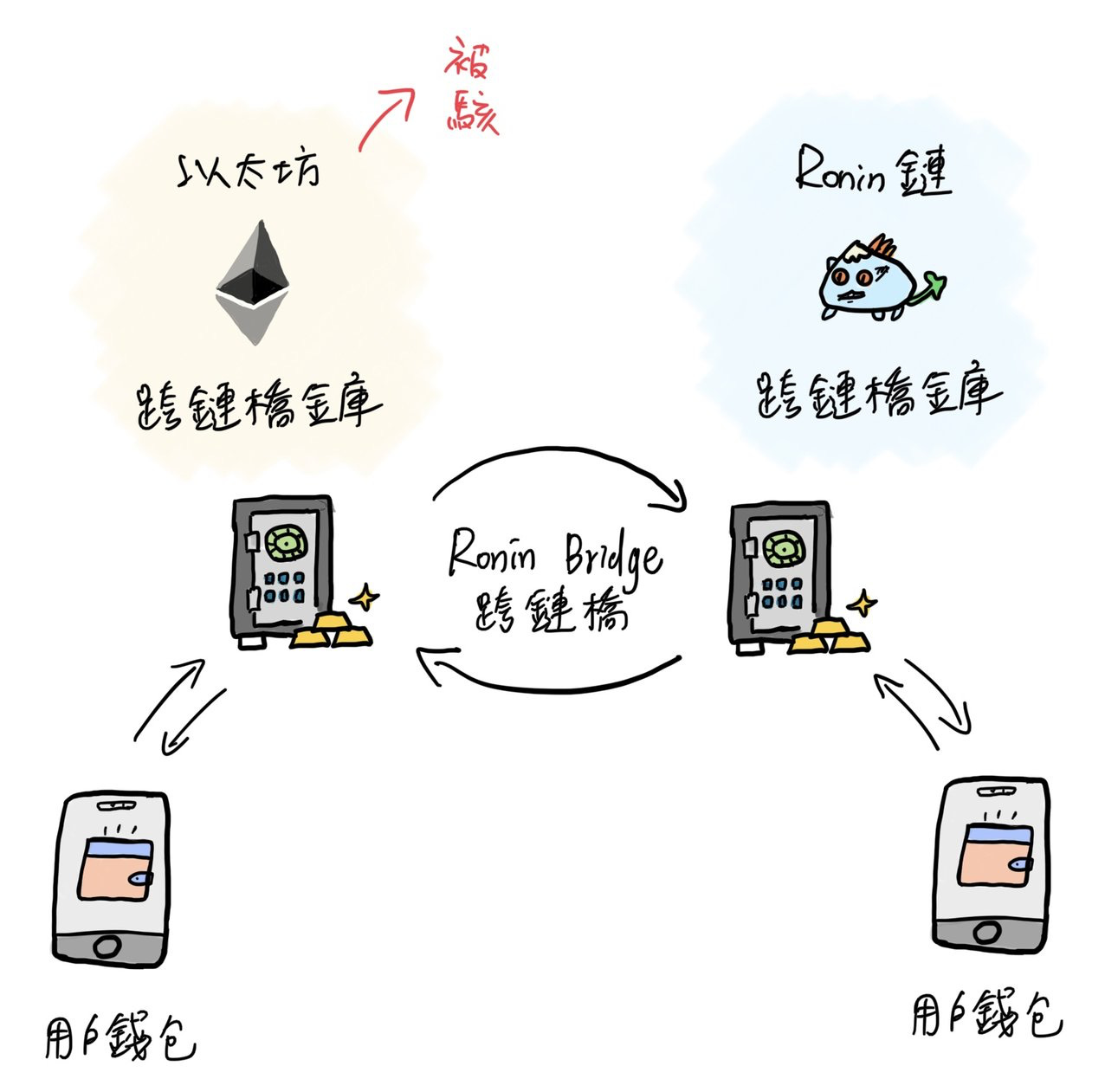
This would bring about many issues. Firstly, poor liquidity would be a problem if each bank (cross-chain bridge) were to issue its own dollar certificates, making it difficult for merchants to decide whose certificates to accept. If a company wants to repatriate a large amount of funds to the United States, a single bank's issued dollar certificate may not be sufficient. Secondly, banks would need to manage large amounts of dollars in the United States to meet cross-border remittance demands. As the amount of cryptocurrency locked by the cross-chain bridge increases, it becomes a more attractive target for hackers.
If the future involves multiple chains coexisting rather than one dominant chain, there is currently a lack of convenient and secure cross-chain services. This is the main reason why Circle launched the Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP) last week.
On-chain Visa
According to Circle's press release:
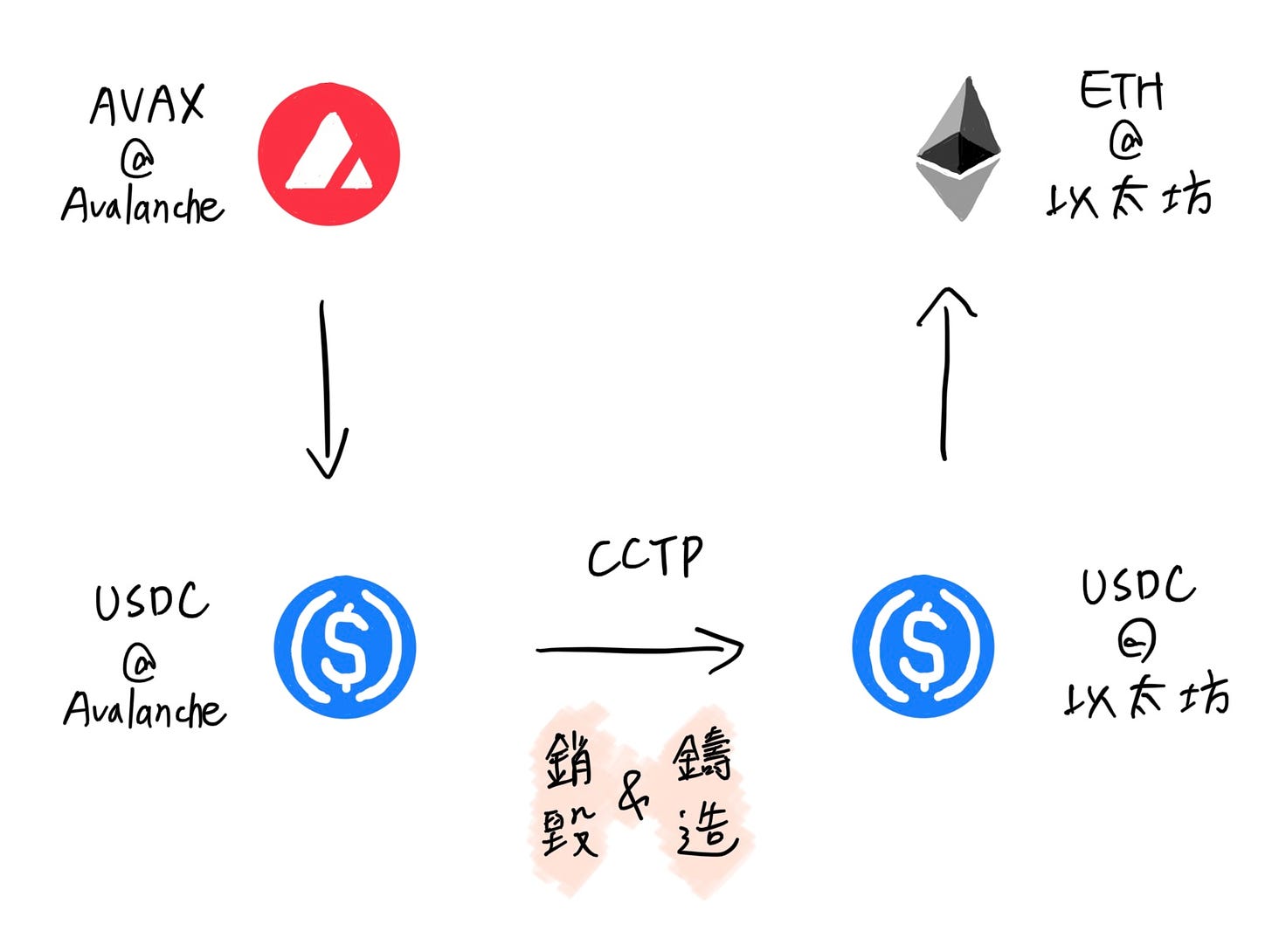
Circle announced today that it will provide Ethereum and Avalanche developers with a cross-chain transfer protocol tool... Applications integrated with CCTP will allow users to complete cross-chain transfers of USDC by burning and minting USDC. By reducing the complexity and risks of traditional lock-and-mint methods, the cross-chain transfer protocol creates a secure and efficient way to transfer assets across chains.
In the future, CCTP will unify USDC liquidity, solving the fragmentation problem caused by multiple cross-chain bridges issuing unofficial USDC in different ecosystems. Additionally, CCTP can provide a simpler and safer payment experience. Users can send and receive USDC without knowing which blockchain their USDC is on.
The functionality of the cross-chain transfer protocol is like an on-chain Visa, making cross-chain transfers simpler.
Visa can provide convenient currency exchange services because it holds multiple fiat currencies and bank accounts in many countries. Centralized exchanges play a role similar to Visa, holding various native cryptocurrencies on different blockchains, and serving as an important channel for cross-chain payments. However, centralized exchanges cannot interact with other smart contracts and are difficult to automate on the blockchain.
This is the main reason why Circle launched the cross-chain transfer protocol. Circle currently issues USDC on 8 blockchains, including Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche. The cross-chain transfer protocol turns Circle's cross-chain minting and burning of USDC into a set of smart contracts, allowing cross-chain bridges, wallets, and even games to complete cross-chain asset transfers through it.
For example, if I want to use Avalanche's AVAX to pay an ETH bill on the Ethereum blockchain, with the cross-chain transfer protocol, it can function like swiping a card, converting my AVAX into ETH on Ethereum to pay the merchant. The behind-the-scenes cash flow involves the "on-chain Visa" first converting AVAX into USDC and burning it, then minting the same amount of USDC on Ethereum and exchanging it for ETH to pay the merchant.
Although the payment process has not been shortened, the security has been greatly improved. The cross-chain transfer protocol eliminates the risk of cross-chain bridges locking up original assets, instead using a burn and mint model. The fewer assets locked by cross-chain bridges, the less the potential loss from hacker intrusions.
Moreover, if a cross-chain bridge's liquidity pool is insufficient, it may result in sending 10 ETH and only receiving 5 ETH on another blockchain. The cross-chain transfer protocol is less likely to have this issue. USDC on each blockchain is issued by Circle and can be exchanged at a 1:1 ratio.
After the emergence of the cross-chain transfer protocol, the first to be affected are the liquidity providers who originally provided funds for cross-chain bridges. They used to deposit cryptocurrencies into cross-chain bridges to help others complete cross-chain asset transfers and earn some fees in return. However, with the cross-chain transfer protocol, cross-chain bridges no longer need to maintain their own liquidity pools, and liquidity providers will be "unemployed."
In an extreme scenario, there may be no need for cross-chain bridges in the future. As long as decentralized exchanges (such as Uniswap) integrate Circle's cross-chain transfer protocol, any currency's cross-chain transactions can be done by first converting assets to USDC, then converting them back after crossing chains. However, those who experienced the USDC crisis earlier in the year may not be so optimistic. After all, USDC is a stablecoin built on a centralized financial system.
Cross-Chain Tokens
Circle's innovative cross-chain transfer protocol has been integrated into many well-known cross-chain bridges, including cBridge, Wormhole, and MetaMask wallet. In addition to basic cross-chain transfers, if lending service Aave also integrates the cross-chain transfer protocol, investors can collateralize ETH on Ethereum and borrow USDC on the Avalanche chain.
Furthermore, although Circle has not explicitly stated, USDC will not only be a USD stablecoin in the future but also an essential tool for completing cross-chain transfers. As more people exchange USDC and trading pairs become more diverse, theoretically, its market value will increase, and Circle can profit from it.
However, I believe that "traditional" liquidity pool-operated cross-chain bridges will continue to exist. The cross-chain transfer protocol is built on USDC, which in turn is built on US banks (and the government). No one in the crypto community likely wants to be choked by the US government - if USDC becomes worthless, cross-chain traffic will be interrupted.
Many people may not have used blockchain applications outside of Ethereum due to the complexity of operations and limited support from exchanges. However, I am optimistic that as the cross-chain transfer protocol supports more blockchains, it will become an essential bridge connecting cross-chain applications.
If Blocktrend's pricing is no longer based on a $8 monthly subscription fee charged by US payment services but instead charged 167,621 Vietnamese dongs by a Vietnamese payment service, you probably wouldn't find it troublesome; just let Visa handle it. The cross-chain transfer protocol is like an on-chain Visa, making the originally complex cross-chain and cross-currency transactions as simple as swiping a card. No matter which blockchain you're on, as long as you convert to USDC first, assets can be transferred across chains!
Blocktrend is an independent media outlet sustained by reader-paid subscriptions. If you think the articles from Blocktrendare good, feel free to share this article, join the member-created Discord for discussion, or add this article to your Web3 records by collecting the Writing NFT.
In addition, please recommend Blocktrend to your friends and family. If you want to review past content published by Blocktrend, you can refer to the article list. As many readers often ask for my referral codes, I have compiled them into a single page for everyone's convenience. You are welcome to use them.